Learning the Types of cactus Fruit helps you understand which cactus plants grow edible fruits and how people use them in daily food culture across desert regions. Many cactus fruits look unusual, taste surprising, and grow on plants that survive harsh heat and dry soil. From prickly pear to dragon fruit, these fruits belong to the cactus family and appear in American deserts, Mexico, and parts of South America.
In this post, you will learn the names, features, and uses of Types of cactus Fruit with pictures, so you can talk about them in food, gardening, and travel topics with confidence.
What is edible cactus fruit
Edible cactus fruit comes from cactus plants that grow sweet, juicy, and safe-to-eat fruits in hot, dry regions. People have eaten these fruits for hundreds of years, especially in the American Southwest and Mexico, where cactus plants are part of daily food life.
How to Eat Cactus Fruit?
Cactus fruit is eaten fresh, cooked, or dried depending on the type. The skin is usually peeled, the seeds may be removed, and the soft pulp is used in salads, juices, jams, or desserts.
Types of Edible Cactus Fruit with Pictures
Cactus fruits grow in many shapes, colors, and flavors. Some taste sweet like watermelon, while others taste mild and refreshing. Below is a list of common edible cactus fruits people learn about in food and plant studies.
Prickly Pear Cactus Fruit
Prickly pear has been eaten by Native American people for thousands of years. It grew wild across the deserts of Arizona, Texas, and Mexico. Early communities used both the pads and the fruit as daily food. The fruit became popular in American markets because it stays fresh in hot weather.

- Scientific name: Opuntia
- Color: Red, purple, yellow, and green
- Taste: Sweet and mildly tangy, like watermelon and berries
- Texture: Juicy with crunchy seeds
- Common uses: Fresh fruit bowls, cactus fruit juice, jelly, candy, and syrup
- Where it grows: Southwestern United States, Mexico, and South America
Dragon Fruit from Cactus Plants
Dragon fruit comes from climbing cactus plants first grown in Central America. Traders carried it to Asia, where it became popular in markets. Today, it is grown in California and Florida for fresh fruit sales.

- Scientific name: Hylocereus
- Color: Pink, red, and yellow skin with white or red flesh
- Taste: Lightly sweet, similar to kiwi and pear
- Texture: Soft with tiny edible seeds
- Common uses: Smoothies, fruit salads, yogurt toppings, and desserts
- Where it grows: United States, Mexico, Vietnam, and Thailand
Saguaro Cacti Fruits
Saguaro fruit has long been part of the diet of the Tohono O’odham people in Arizona. Every summer, families harvested the fruit using long wooden poles. The fruit symbolized the start of the rainy season and community gatherings.
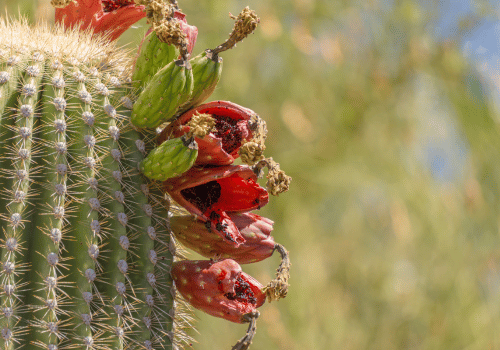
- Scientific name: Carnegiea gigantea
- Color: Deep red inside
- Taste: Rich and sweet, like ripe berries
- Texture: Thick pulp with many seeds
- Common uses: Syrup, jam, and traditional drinks
- Where it grows: Sonoran Desert in Arizona and Mexico
Barrel Fruit Cactus
Barrel cactus fruit was used by desert travelers as an emergency food source. Its bright yellow flowers later turned into edible fruit. Native communities learned which barrel cactus fruits were safe to eat and how to prepare them.
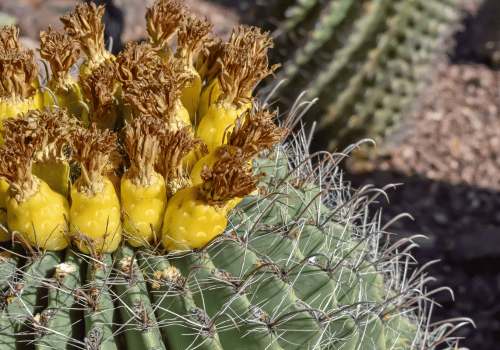
- Scientific name: Ferocactus
- Color: Yellow to orange
- Taste: Mild and slightly sour
- Texture: Soft pulp
- Common uses: Fresh eating and desert survival food
- Where it grows: Southwestern United States and Mexico
Organ Pipe Cactus Fruit
Organ pipe cactus fruit has been harvested in the deserts of Arizona and Mexico for centuries. Families collected the fruit in summer and dried it for later use. It became part of traditional desert recipes.

- Scientific name: Stenocereus thurberi
- Color: Red flesh
- Taste: Sweet like raspberries
- Texture: Juicy with small seeds
- Common uses: Fresh fruit, jams, and drinks
- Where it grows: Arizona and northern Mexico
Cardón Cactus Fruit
Cardón cactus is the tallest cactus in the world. People living in Baja California used its fruit for food and medicine. The fruit helped travelers survive long desert journeys.

- Scientific name: Pachycereus pringlei
- Color: Red and purple
- Taste: Sweet and refreshing
- Texture: Soft and juicy
- Common uses: Fresh eating and juice
- Where it grows: Baja California and Sonoran Desert
Cholla Cactus Fruit
Cholla buds and fruits were important food for desert people. The buds were dried and stored for winter meals. Over time, cholla fruit became a traditional desert food.

- Scientific name: Cylindropuntia
- Color: Green to yellow
- Taste: Mild and slightly earthy
- Texture: Soft when cooked
- Common uses: Cooked vegetable dishes and salads
- Where it grows: Southwestern United States and Mexico
Peruvian Apple Cactus Fruit
Peruvian apple cactus was first grown in South America. Farmers later brought it to California for home gardens and fruit farms. Its night flowers and sweet fruit made it popular.
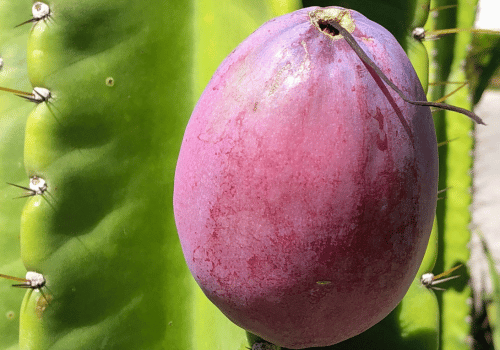
- Scientific name: Cereus repandus
- Color: Red skin with white flesh
- Taste: Sweet and crisp
- Texture: Apple-like pulp
- Common uses: Fresh slices, fruit bowls, and juices
- Where it grows: California, Florida, and South America
Cacti Strawberry Pear
Strawberry pear is another name for a type of prickly pear. Early settlers compared its taste to strawberries. The name helped people remember the fruit easily.

- Scientific name: Opuntia ficus-indica
- Color: Red and pink
- Taste: Sweet like strawberries
- Texture: Juicy with seeds
- Common uses: Desserts, smoothies, and jams
- Where it grows: United States and Mexico
Types of Night Blooming Cactus Fruit
Night blooming cactus plants open their flowers after sunset and grow edible fruit later. These fruits are common in warm desert regions and home gardens.
Queen of the Night Cactus Fruit
Queen of the night cactus became famous for its one-night-only flowers. Gardeners noticed the fruit that followed the bloom and began eating it. The fruit became part of home garden harvests.
- Scientific name: Epiphyllum oxypetalum
- Color: Purple to red
- Taste: Mild and sweet
- Texture: Soft pulp
- Common uses: Fresh eating and fruit drinks
- Where it grows: California and tropical regions
Peruvian Apple Cactus Fruit (Night Blooming)
This cactus blooms at night and produces sweet fruit by morning. Gardeners in California grow it for both flowers and fruit. It became a popular backyard fruit plant.
- Scientific name: Cereus repandus
- Color: Red skin with white flesh
- Taste: Sweet and crisp
- Texture: Crunchy pulp
- Common uses: Fresh slices and fruit salads
- Where it grows: Southern United States
Rare Edible Cactus Fruit Varieties
Some cactus fruits are harder to find but still safe and tasty to eat. These rare varieties grow in special climates and are often grown by collectors.
Blue Myrtle Cactus Fruit
Blue myrtle cactus was grown in early botanical gardens for its blue stems. People later discovered its fruit was edible. It became a favorite in warm climate gardens.
- Scientific name: Myrtillocactus geometrizans
- Color: Purple berries
- Taste: Sweet like blueberries
- Texture: Soft berries
- Common uses: Fresh eating and jams
- Where it grows: Mexico and California
Old Man Cactus Fruit
Old man cactus is known for its white hair-like spines. Gardeners later noticed its small edible fruits. The fruit added value to this unusual plant.
- Scientific name: Cephalocereus senilis
- Color: Pink to red
- Taste: Mild and sweet
- Texture: Soft pulp
- Common uses: Fresh fruit and small desserts
- Where it grows: Mexico and warm US states
FAQs People Often Ask
No, only certain cactus species grow safe edible fruits. Always check the plant name before eating.
Prickly pear tastes sweet and juicy, similar to watermelon mixed with berries.
Yes, dragon fruit grows on a climbing cactus plant called Hylocereus.
Most cactus fruits contain small edible seeds inside the soft pulp.
They grow mainly in Arizona, California, Texas, and parts of Florida.
Read more