Papaya grows in many forms, sizes, and flesh colors, and each type behaves a little differently when ripe. The types of papaya fruit vary by shape, sweetness, seed cavity size, skin thickness, and inner flesh tone. Some varieties stay small and soft, while others grow large and firm, making them useful for different eating and cooking needs.
In this post, you’ll learn how to handle papaya correctly and understand Types of Papaya Fruit through names, traits, and pictures. Knowing these names helps in grocery shopping, farming discussions, nutrition topics, and everyday food conversations.
How to cut a papaya fruit?
Cutting papaya properly keeps the flesh neat and removes bitter seeds safely. Many beginners press too hard or cut unevenly, which damages the soft center. Below is a simple way to handle the fruit cleanly and confidently.
Below is a step-by-step method that explains how papaya is usually cut at home or in kitchens.
- Wash the papaya under running water to remove surface residue
- Place it lengthwise on a stable cutting board
- Slice the fruit in half from top to bottom
- Scoop out the seeds using a spoon
- Peel the skin away or slice the flesh directly
- Cut into cubes or long slices as needed

How to eat papaya?
Papaya can be eaten fresh, chilled, or lightly seasoned depending on ripeness. Ripe papaya feels soft when pressed and smells slightly sweet near the stem area.
Below is a easy guide of common eating methods.
- Eat fresh slices after removing seeds
- Add lime juice for a balanced taste
- Mix cubes into fruit bowls
- Chill before eating for a softer texture
- Mash lightly for smoothies
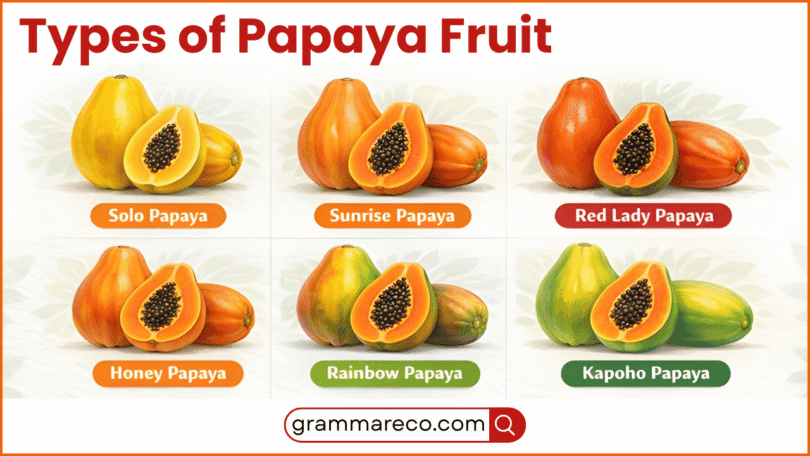
Types of Papaya Fruit with Facts and Images
Papaya varieties differ by growing region, genetics, and farming purpose. Some types are bred for sweetness, while others focus on size or firmness. Below are widely known papaya fruit types, each explained with key traits to help learners recognize them easily.

Types of Papaya Fruit with Information and Images
Papaya comes in several varieties, each with unique traits. Below is a list of the most common types grown around the world, with their characteristics and typical uses.
Solo Papaya
Solo papaya is a small, sweet fruit originally from Hawaii. Its compact size and smooth texture make it ideal for snacks or fresh salads. Solo papayas are popular for personal consumption and household gardens.

- Appearance: Smooth, thin skin, typically yellow-orange with a slightly elongated shape, easy to peel.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Solo’
- Texture: Soft, juicy, and creamy, melts easily in the mouth.
- Fruit size: 1–2 pounds, usually single-serving size.
- Seeds: Small, black, and edible but slightly bitter.
- Maturity: Ready to eat in 6–8 months after planting.
- Uses: Eaten fresh, in fruit bowls, smoothies, desserts, and as a tropical snack.
Sunrise Papaya Species
Sunrise papaya is medium-sized with a rich orange flesh. Known for its sweetness and slightly tangy flavor, it is popular in tropical and subtropical regions. Sunrise papayas are often served in breakfast dishes and fresh fruit platters.

- Appearance: Bright yellow-orange skin, slightly elongated shape, smooth surface.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Sunrise’
- Texture: Soft yet firm, juicy, melts slowly in the mouth.
- Fruit size: 2–3 pounds, medium-sized fruit.
- Seeds: Small, black, gelatinous seeds in the center cavity.
- Maturity: 7–9 months, best consumed when fully yellow.
- Uses: Fresh eating, smoothies, salads, and tropical desserts.
Red Lady Papaya
Red Lady papaya is widely cultivated for its bright red-orange flesh and sweet taste. It grows quickly and produces high yields, making it a favorite for home gardens and commercial farms.
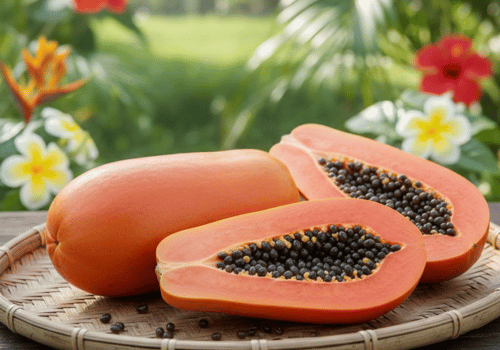
- Appearance: Red-orange flesh, yellowish-orange skin, oval shape, smooth surface.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Red Lady’
- Texture: Soft and juicy, yet firm enough to slice cleanly.
- Fruit size: 2–4 pounds, medium to large size.
- Seeds: Black, round, edible but slightly pungent.
- Maturity: 6–8 months, often harvested while slightly green for transport.
- Uses: Eaten fresh, in salads, smoothies, or desserts, also used in tropical cooking.
Maradol Papaya
Maradol papaya is large and elongated, with sweet orange flesh. It is mostly grown in Mexico and Central America and used for both fresh consumption and processing into juices.

- Appearance: Green to yellow-orange skin when ripe, smooth, elongated shape.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Maradol’
- Texture: Firm yet juicy, slightly fibrous near the center.
- Fruit size: 5–10 pounds, large fruit.
- Seeds: Large, black, gelatinous, often discarded.
- Maturity: 9–12 months, requires careful harvesting.
- Uses: Fresh eating, juices, cooking, preserves, and tropical fruit salads.
Tainung Papaya
Tainung papaya is a high-yield hybrid variety from Taiwan, known for uniform size and sweet orange flesh. It is widely grown for commercial purposes due to its excellent shelf life.

- Appearance: Smooth, bright yellow-orange skin, cylindrical shape, slightly tapered ends.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Tainung’
- Texture: Soft, juicy, smooth, minimal fibrous texture.
- Fruit size: 4–7 pounds, medium-large fruit.
- Seeds: Black, small, concentrated in central cavity.
- Maturity: 8–10 months, harvested when skin fully yellow.
- Uses: Fresh eating, juice production, desserts, and culinary dishes.
Honey Papaya or Coorg Honey Dew Variety
Honey papaya is known for its exceptionally sweet, golden-orange flesh and smooth texture. This variety is compact and easy to grow in home gardens. Its high sweetness makes it popular for fresh eating and desserts.

- Appearance: Golden-orange skin, smooth and thin, slightly elongated shape, easy to peel.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Honey’
- Texture: Soft, juicy, and very sweet, melts in the mouth.
- Fruit size: 2–3 pounds, medium-sized fruit.
- Seeds: Small, black, gelatinous, edible but slightly bitter.
- Maturity: 7–8 months, ready to eat when fully golden.
- Uses: Fresh consumption, smoothies, desserts, tropical fruit salads, and breakfast bowls.
Waimanalo Papaya Fruit
Waimanalo papaya is a Hawaiian variety prized for its bright orange flesh and rich, sweet flavor. It grows well in tropical climates and is often used for fresh eating and juice production.

- Appearance: Bright orange skin with smooth texture, cylindrical to slightly tapered shape.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Waimanalo’
- Texture: Soft and juicy, slightly fibrous near the center.
- Fruit size: 3–5 pounds, medium-large fruit.
- Seeds: Black, small, gelatinous, slightly pungent taste.
- Maturity: 8–10 months, harvested when fully ripe.
- Uses: Fresh eating, smoothies, juices, salads, and tropical cooking.
Rainbow Papaya Variety
Rainbow papaya is a hybrid variety with vibrant multi-colored flesh ranging from yellow to deep orange-red. It is visually appealing and moderately sweet, often used for fresh consumption and garnishing.

- Appearance: Smooth skin, yellow to orange-red, slightly oval-shaped, visually striking.
- Scientific classification: Carica papaya ‘Rainbow’
- Texture: Soft and juicy with consistent sweetness throughout.
- Fruit size: 3–6 pounds, medium to large fruit.
- Seeds: Black, small, concentrated in the center cavity.
- Maturity: 8–9 months, ready when skin shows uniform color.
- Uses: Fresh eating, fruit platters, tropical desserts, and decorative garnishing.
Papaya Species based on flesh color
Papaya flesh color affects taste, aroma, and common use. Some colors signal sweetness, while others suggest mild flavor. Below are the main flesh-based groups learners often hear about.
Red papaya variety
Red-fleshed papaya types are known for higher sugar content and strong aroma. These papayas feel softer when ripe and often taste richer. Common names include Red Lady, Maradol, Tainung, and Sunrise. They are often used for fresh eating, juices, and fruit bowls in the US market.
Orange papaya types
Orange-fleshed papaya types balance sweetness and firmness. The texture holds well after cutting, making them good for salads. Solo papaya, Kapoho, and Waimanalo fall into this group. Their color looks bright and inviting when sliced, which suits visual food presentation.
Yellow papaya Fruit
Yellow-fleshed papaya types taste milder and slightly less sweet. These varieties are often used in cooking or mixed dishes. They stay firmer when ripe and work well for light sauces or blended preparations where sweetness is not dominant.
Papaya fruit types based on taste profile
Taste plays a major role in how papaya is chosen and used. Some people prefer strong sweetness, while others like mild flavor. Below are the main taste-based groupings.
Sweet papaya varieties
Sweet papaya varieties have high natural sugar and soft flesh. They release aroma quickly when ripe. Red Lady, Sunrise, Solo, Kapoho, and Maradol are common sweet types. These are often eaten fresh without seasoning and are popular in breakfast plates.
Mild flavored papaya variety
Mild flavored papaya varieties taste gentle and slightly neutral. The flesh feels firmer and less aromatic. These papayas are often paired with lime or spices. They are also used in cooking where sweetness should not overpower other ingredients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, papaya seeds are edible but have a slightly bitter taste and are often used in small amounts.
Maradol and Tainung varieties are preferred for juice due to large size and smooth, juicy flesh.
Solo and Sunrise are ideal for salads as they are soft, sweet, and easy to cut into cubes.
Yes, dogs can eat papaya in small amounts. It is safe and provides vitamins and fiber, but remove seeds and skin first. Feeding too much can cause stomach upset, so give it as an occasional treat for dogs like Max or Bella.
A papaya is ripe when its skin turns yellow or orange, it feels slightly soft when gently pressed, and it has a sweet aroma near the stem. Avoid green or very hard papayas, as they are not fully ripe.
Read more